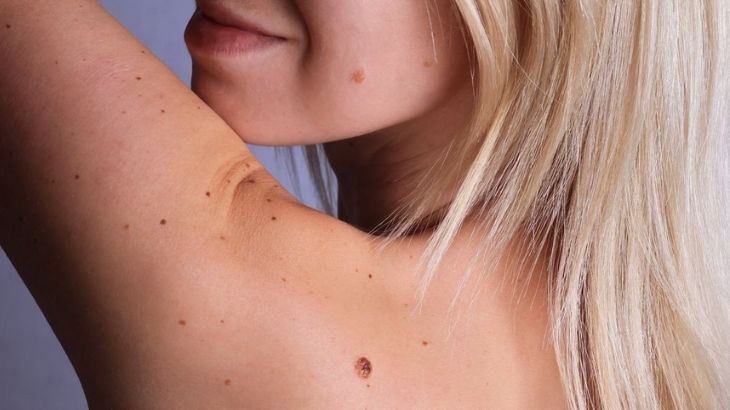
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer originating from pigment producing cells called melanocytes. When these cells are damaged by radiation they can transform and behave abnormally. If there is enough permanent DNA damage, then these pigment cells can multiply and grow without regulation and become a cancer. Unfortunately, this cancer is notorious for camouflaging amongst other skin lesions, and due to it’s lack of symptoms a melanoma can grow and metastasize in silence.
Who is at risk?
Melanoma occurs 1 in 40 people in lighter skin types and less frequently in darker skin types in all age groups. There are two major components of melanoma development: Genetic and Environmental Factors. Since hereditary plays a major role, knowing if you have a family history of melanoma is extremely important. Additionally, environmental exposures can alter the normal biology. For example, exposing skin to radiation from the sun, tanning beds, and various occupations such as welding, radiology, outdoor work can lead to DNA damage resulting in melanoma or other skin cancers.
Are all skin cancers melanoma?
NO. There are several skin cancers of the skin, and melanoma is just one of the many types. Melanoma is the third most common skin cancer, preceded by basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It is important to distinguish between these cancers because melanomas are more aggressive and have an increased risk of metastasis-spreading to other organs.
How to detect melanoma?
Since melanoma are discrete, they are very difficult to detect by the untrained eye. Additionally, it very difficult to self inspect one’s back, which is one of the most common sites for melanoma to occur.
A guideline to help is the ABCDE‘s of melanoma. Moles with the following need to be professionally evaluated:
- Asymmetry
- Borders irregular
- Color uneven
- Diameter greater than 4mm
- Evolution (changing) moles
It may look like an age spot, a bruise, a sore, a cyst, a scar or a dark line beneath your nail. You may not feel a melanoma, but there are times that it may itch, hurt or bleed. If there is a concern about melanoma, it is important to have your skin checked head to toe by a Board Certified Dermatologist regularly.
Keywords: Melanoma, Moles, Moles Treatment in Alabama, Moles Treatment by Dermatology in Alabama, Skin Cancer, Skin Cancer Treatment by Moh’s Specialist in Alabama, Mohs Surgery for Skin Cancer